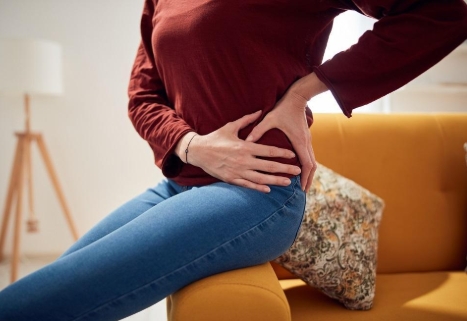
If you spend long hours sitting at a desk or lying on your side while sleeping, you may be familiar with the dull, uncomfortable sensation of hip pain. This type of pain typically originates from issues within or around the hip joint, which connects the thigh bone (femur) to the pelvis. According to the Cleveland Clinic, hip pain affects about 10% of the general population, and its prevalence increases with age.
So, what causes hip pain? The reality is that there are many different potential causes. While it often stems from issues with the tissues surrounding the hip joint, such as cartilage, muscles, and tendons, hip pain can also result from conditions affecting other parts of the body. Cleveland Clinic explains that the pain can manifest in different areas of the hip, such as the front near the groin, the back near the buttock, or along the sides. The exact symptoms will vary depending on the underlying cause and may include clicking, snapping, cramping, or a burning sensation.
The reasons behind hip pain often depend on the person’s age. For younger individuals or athletes, hip impingement is a common cause. This occurs when there’s a tear in the labrum (the tissue surrounding the socket) or a pinching in the joint. As people age, hip arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis, becomes more prevalent. This condition involves the loss of cartilage, which leads to pain, inflammation, and difficulty with movement.
In addition to these conditions, inflammation of muscles and tendons around the hip joint, like the hip flexors and abductors, is another common cause of pain. Simple activities such as walking, sitting for extended periods, or bending the hip can aggravate the pain.
Another potential cause of hip pain is bursitis, an inflammation of the bursa, the protective cushioning where tendons meet bone. This condition often affects the outer hip and can be worsened by pressure, such as lying on the side while sleeping.
Understanding the exact cause of your hip pain is crucial, as treatment can vary depending on whether it’s related to muscle strain, arthritis, impingement, or bursitis.